
Introduction
As most of us know the HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is a stateless protocol, meaning that there is no link between two requests being successively carried out on the same connection. Nevertheless, in some situation we need to remember the request sender as shown the following example :
Imagine we have an e-commerce website and a user adds a product to his shopping cart and after he navigates to another page, the product disappears from the shopping cart.
So in order to solve this problem, we need to make the application remember the user identity by implementing JWT token or Session.
Authentication
Before talking about Sessions or JWT we need first to define the authentification which is a process of identifying the user identity in a web application, in other words, check if the user exists in the database then let him access the resources, if not show an error message.
It answers the question: Who are you?
Authorization
After a good authentication, the server needs to verify the user’s permissions, in other words, what the user can do, and cannot do in your application.
It answers the question: What can you do?
Session-Based Authentication
In the session-based authentication, the server creates a session for each user authenticated and keeps all information about the session in a table located in the server, this table holds two columns the first one for the session id and the second for the session information.
After the session creation, the server will store the session id on a cookie in the browser’s client, and when the user wants to send a request he needs to send also the cookie that holds the session id so that the server can know the user identity.
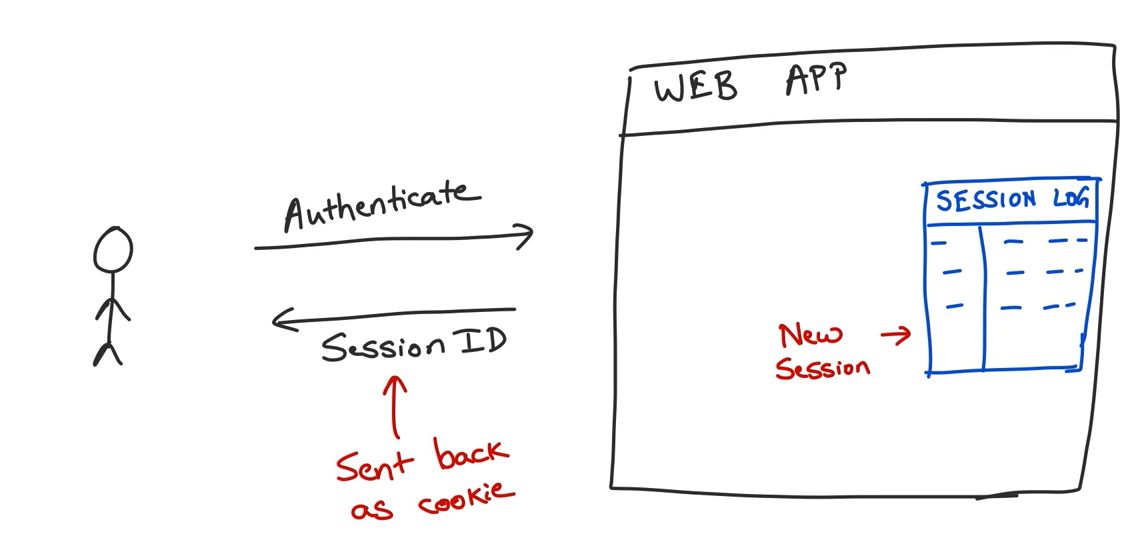
Cookies: are small files on a user’s computer containing pairs of (key, data) values and can be accessed either by the web server or the client computer. For more details, you can visit this link: Click Here
This type of authentication is called stateful because sessions are stored on the server-side:
- memory (file system …)
- cache (REDIS or Memcached …)
- DB (Postgres, MongoDB …)
Let’s see the workflow for the session authentication:
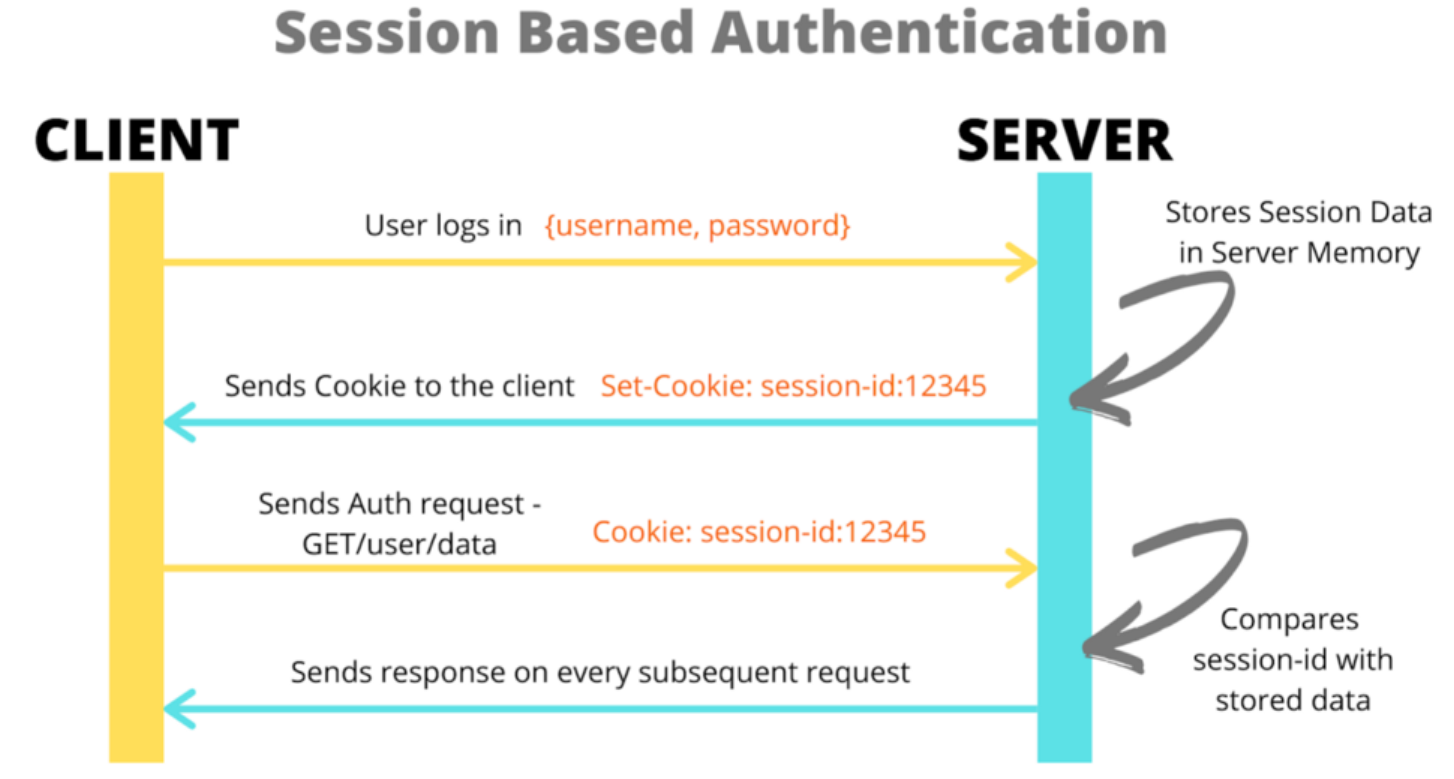
- User make a POST request to send his login and password.
- Server verifies the credentials from the database.
- Server stores session data in the memory, cache, or DB.
- Sever issues a cookie with a session ID.
- User sends the cookie along with each request.
- Server verifies the user identity using session id.
- When the user logs out the session will be destroyed and the server clears the cookie.
Token-Based Authentication using JWT
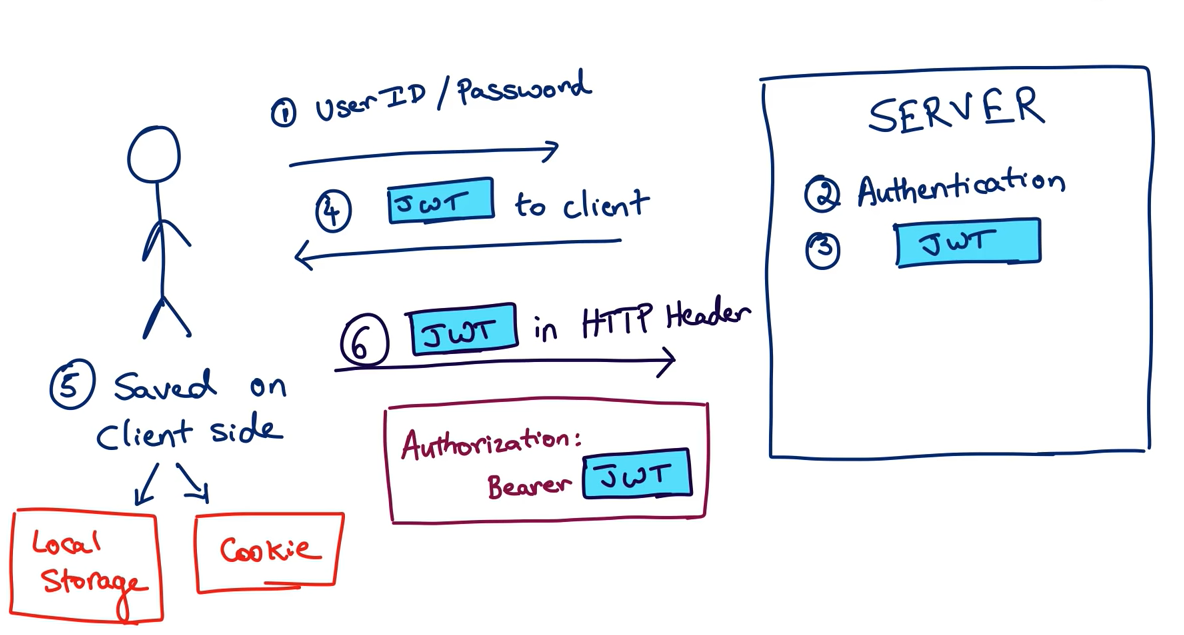
As you can see in the Session-based authentication, when the user is authenticated the server creates a session for this user, now instead of creating the session id and information for a user, the server creates a token JWT which is usually stored in the local storage of the user and whenever the user sends a request he sends also this token in the header of the request. The server would then validate the JWT with every request from the client and sends a response.
JSON web token or JWT is a token by which the server and the client can securely exchange data, this token consists of three parts header, payload, and signature for more details about the creation of this token you can check this link: jwt.io
This type of authentication is called stateless because the server doesn’t store the user token, the server needs to maintain no state, everything is stored on the client-side.
Let’s see the workflow for the token-based authentication:
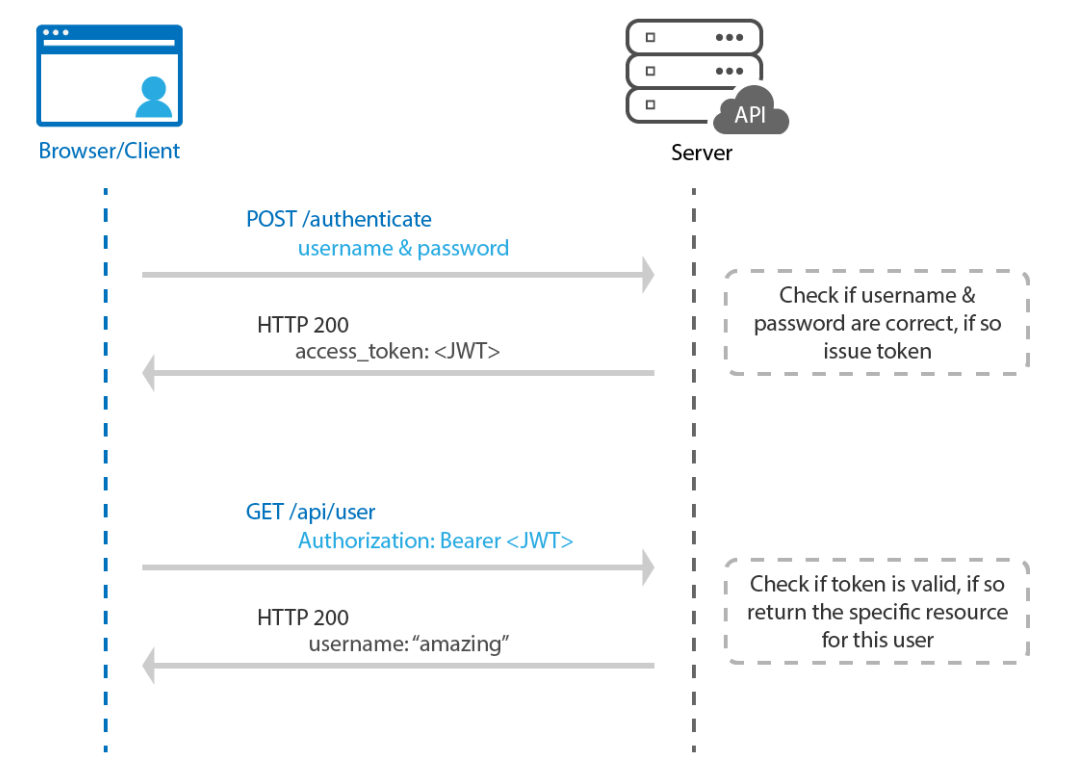
- User make a POST request to send his login and password.
- Server verifies the credentials from the database.
- Sever generates a temporary token and embeds user data into it.
- Server responds with the token (in response body or header).
- User stores the token in client storage.
- User sends the token along with each request.
- Server verifies the token & grants access.
- When the user logs out, the token is cleared from client storage.
Summary
For the current Web application, the Token-based authentication is more recommended, but you need to pay attention to make JWT take just the necessary information about the user and sensitive information should be omitted to prevent XSS (cross-site scripting) security attacks.
And you need to keep in your mind that the authentication process can be stateful using i.e Cookies-Session Duo, or stateless i.e using JWT.
That was all for this blog !! 😀😀