
Introduction
Hello everyone!! 😃😃
In this blog, I will talk about one of the most popular ORM frameworks in the Java ecosystem, which is Hibernate, but I will mainly focus on the architecture of this framework, the core components, and their functionalities.
So let’s get started.
💡 ORM or object-relational mapping is the programming technique to map application domain model objects to the relational database tables.
What is JPA?
Before talking about Hibernate, we need first to understand the JPA.
JPA or Java Persistence API is a standard for mapping Java objects to relational databases, which means that each object is represented as a table in the database, in other words, the Java objects can outlive outside the Java application and the JPA specification lets you define which objects should be persisted, and how those objects should be persisted in your Java applications, as well as via the JPA the developer can map, store, update, and retrieve data from relational databases to Java objects and vice versa.
💡 JPA specifications are defined with annotations in
javax.presistence package.
Whereas we have some problems here because the JPA is just a specification, meaning there is no implementation. You can annotate your classes as much as you would like with JPA annotations, however, without implementation, nothing will happen.
We can think that JPA is an interface but in order to work with it, we need an implementation.
JPA implementations (Hibernate)
As you can see, in the section above we found out a problem which is the implementation of JPA, but don’t worry JPA has many implementations such as EclipseLink ,Apache OpenJPA and Hibernate framework which is the most popular.
So, from everything we’ve seen, we can define Hibernate as Java-based ORM tool that provides a framework for mapping application domain objects to the relational database tables and vice versa, moreover by Hibernate we can manipulate data from relational databases to Java objects without working with the SQL because Hibernate contains predefined methods for creating, updating, deleting, inserting objects from and to database tables.
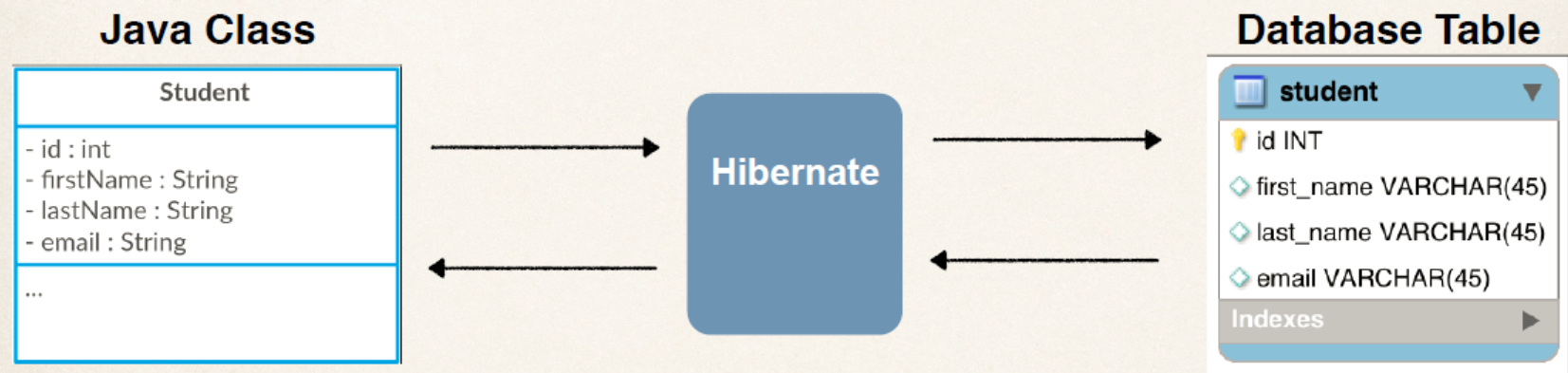
Hibernate architecture

As you can see in the picture Hibernate holds several components. In this section I will try to clarify each component and it’s role:
Configuration object: org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration is a predefined class which holds configuration properties of Hibernate, it’s created first when creating the Hibernate application, it has two components:
- Database connection which provides the configuration for the connection.
- The class mapping setup which creates the connection between the java class and the database.
SessionFactory object: It is instantiated by the Configuration Object, it’s a factory of Session and client of ConnectionProvider. It holds second-level cache (optional) of data.
The org.hibernate.SessionFactory interface provides factory methods to create objects of Session.
👉 Note: We can have one
SessionFactoryper database, so if we want to work with multiple databases, we need multipleSessionFactoryand for each SessionFactory a configuration file.
Session object: It is considered as an interface between the data stored in the database and the application. It is a short-lived object that wraps the JDBC connection also it’s a factory of Transaction, Query, and Criteria as well as the org.hibernate.Session interface provides methods to insert, update, and delete the objects. It holds the first-level cache (mandatory) of data.

Transaction: The org.hibernate.Transaction interface provides methods for transaction management and handles the transaction works in the Hibernate framework.
Query object: The org.hibernate.query.Query interface used to manipulate the persistent objects (creation, retrieving data …) using SQL or HQL.
👉Note: HQL or Hibernate query language is an object-oriented query language, similar to SQL, but instead of operating on tables and columns, HQL works with persistent objects and their properties.
Criteria object: org.hibernate.Criteria interface is also used to manipulate the persistent object but by executing the object-oriented criteria queries, meaning that this interface provides predefined methods to add criteria to a query.
Hibernate benefits
- Hibernate eliminates all the boiler-plate code that comes with JDBC.
- Hibernate cache helps us in getting more performance.
- Hibernate provides a powerful query language (HQL).
- Easy integration of Hibernate.
- Hibernate support lazy initialization using proxy objects.
Conclusion
I know that there is a lot of to say and understand in Hibernate framework but I tried in this blog to give you just the most important points of this framework, I will try in the future blogs to focus more on details(implementations).
I hope you understand all the points that we have touched on, if you find this blog interesting don’t hesitate to share it with your friends. 😃😃